
Early Childhood Development (ECD) is an outcome that defines a child’s status as being appropriately nourished, physically healthy, mentally alert, emotionally sound, socially competent, and ready to learn.
There is a need to extend our focus on the determinants of ECD beyond the first 1000 days to better identify the sensitive periods of each determinant. More prospective, longitudinal studies are needed to quantify the associations between early life experiences with later mental health outcomes, as an attempt to determine the aetiologies and progression of common mental health disorders.
“COINCIDE aims to address these major research gaps by simultaneously assessing a broad range of exposure relevant to ECD, to determine their impact on neurodevelopmental and mental health outcomes across the first decade of life.“
Nurturing Care Framework
A framework for helping children survive and thrive to transform health and human potential.
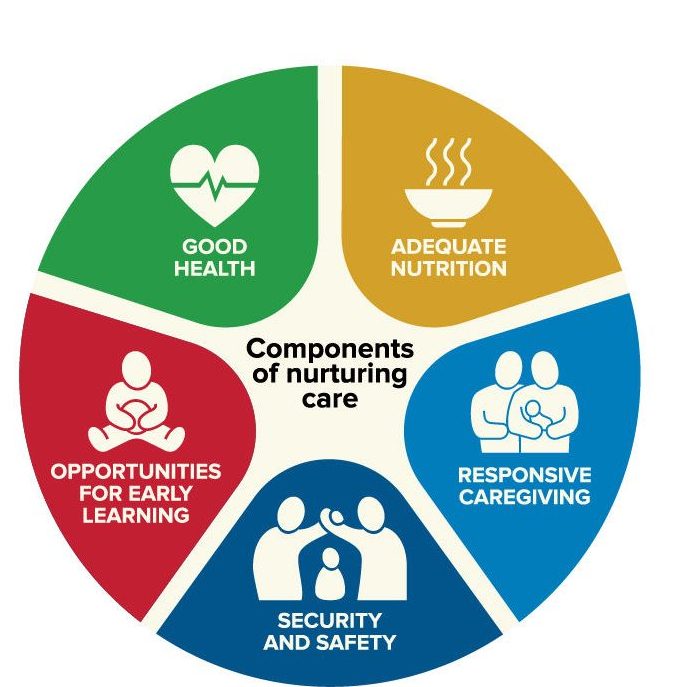
Nutrition, Health, Safety and Security, Early Learning, and Responsive caregiving are crucial domains of the Nurturing Care Framework.
An enabling atmosphere is necessary for the Nurturing Care Framework to be implemented. Although families generally implement nurturing care through home-based methods, there has been an increase in out-of-home care for very young children, frequently in childcare facilities, as a result of shifting family dynamics and a rise in maternal employment. Therefore, support for families and childcare providers is necessary to ensure that caregivers have the physical and emotional health, resources, and capacity to offer Nurturing Care for children.
Nurturing Care Resources
COUNTRY PROFILE-INDIA
UNICEF and Countdown to 2030 Women’s, Children’s, and Adolescent’s Health collaborated to establish the “Country Profiles for Early Childhood Development.” In an effort to offer a baseline against which development can be gauged, the profiles strive to gather all relevant data for both national and international monitoring in one location. Every year, the profiles are updated. In May 2018, the Nurturing Care Framework and an initial set of 91 nation profiles were both released. In 2019, the set was updated and expanded to include 138 low- and middle-income nations. In 2020, the list was updated and expanded once more.
The Nurturing Care Handbook was created by partners including the World Health Organization and UNICEF. The Handbook’s five strategic actions serve as its organizing principles, just like the Nurturing Care Framework. Overviews, suggested actions, common barriers, tools and checklists for typical tasks, indicators for tracking progress, links to useful articles and websites, and case studies demonstrating how governments and other stakeholders around the world can put nurturing care into practice are all included in the guides for each strategic action. This publication takes into account comments made on a draught of the Handbook that was made available in January 2021.
The Nurturing Care Practice Guide is intended for managers and service providers who, at any level, are in charge of or offer health and nutrition services to young children and their caregivers. It responds to inquiries from practitioners and national teams who have learnt about the Nurturing Care Framework and want to understand how to adapt health and nutrition services to be supportive of nurturing care and strengthen caregivers’ capacity.
Five Components of Nurturing Care Framework

Responsive Caregiving
Responsive caregiving is a term that simply refers to parents and caregivers supporting the learning of babies by sitting close to babies during play and offering verbal and non-verbal gestures to communicate support and assurance as the baby explores and plays.

Nutrition
Nutrition is a critical part of health and development. Better nutrition is related to improved infant and child mental health, and stronger immune systems. Healthy children learn better. People with adequate nutrition are more productive and can create opportunities to break the cycles of poverty and hunger.

Safety & Security
Clean, safe, and secure environments contribute to enabling environments for nurturing care. Clean air, safe and secure surroundings, and outlets for physical activity are essential conditions for children to survive and thrive.

Early Learning
Early learning has a significant impact on how a child develops throughout their lifetime. While it may appear that learning begins when kids start going to school, it actually begins from birth. Because of this, it’s crucial to provide your child with a safe atmosphere in which to learn and develop.

Health
Early health supports growing biological systems that enable children to flourish and develop into healthy people. Positive early experiences lay the groundwork for children to develop strong brain architecture, which supports a wide range of abilities and learning capacities over the course of a lifetime.

“Children with a shaky early foundation find each early developmental step harder. The difference between children with a strong beginning and children without an early foundation is growing quickly, and it becomes difficult to cross as time goes on.”
— Dr. Malak Alori, Women & Child Health Directorate Director, Ministry of Public Health, Jordon
